Cerebral blood flow infrastructure network
Department of Cell Biology and Molecular Medicine, University of Szeged, Hungary
Experimental electrophysiology and cerebral blood flow imaging workstation
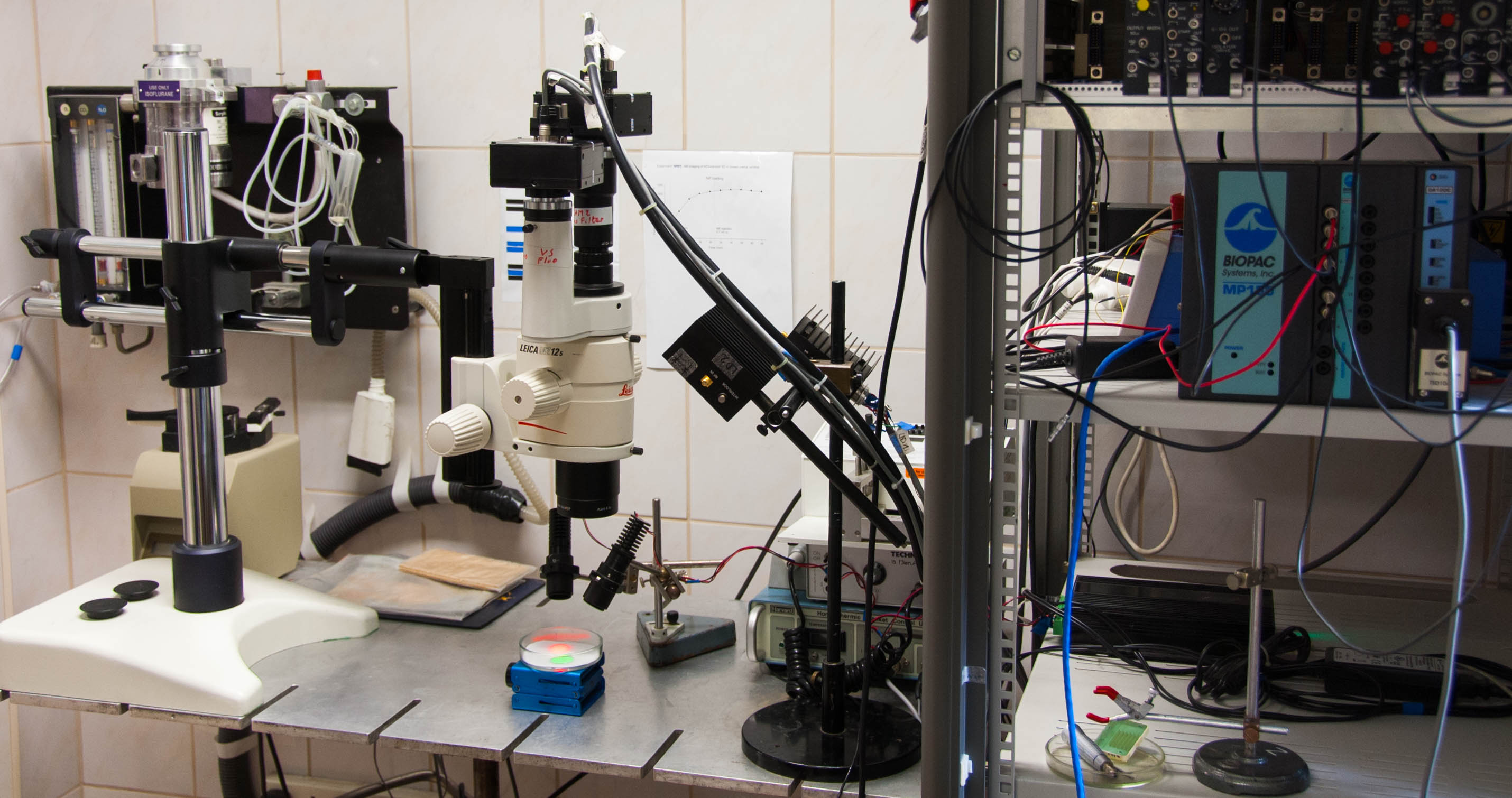 Electrophysiological data acquisition is supported by a NeuroLog System (Digitimer Ltd, United Kingdom), which include pre-amplifiers (NL102G, NL100AK), differential amplifiers (NL106 or NL107), and filter and conditioner modules (NL125, NL144 or NL530). The system is complemented with a high-quality noise eliminator (HumBug, Quest Scientific Instruments Inc., Canada). Instruments for analog/digital (A/D) signal conversion are MP150 (Biopac Systems Inc., USA) or an A/D converter card NI USB-6008/6009 (National Instruments, Austin, Texas, USA).
Electrophysiological data acquisition is supported by a NeuroLog System (Digitimer Ltd, United Kingdom), which include pre-amplifiers (NL102G, NL100AK), differential amplifiers (NL106 or NL107), and filter and conditioner modules (NL125, NL144 or NL530). The system is complemented with a high-quality noise eliminator (HumBug, Quest Scientific Instruments Inc., Canada). Instruments for analog/digital (A/D) signal conversion are MP150 (Biopac Systems Inc., USA) or an A/D converter card NI USB-6008/6009 (National Instruments, Austin, Texas, USA).
Laser-Doppler flowmetry (LDF) is conducted with a PeriFlux 5000 system (Perimed AB, Sweden).
Devices of the custom-made optical imaging setup include high-power LED light sources (Mightex Systems, Pleasanton, CA, USA) with filters (Omega Optical Inc. Brattleboro, VT, USA), laser diodes (Thorlabs Inc., New Jersey, USA) driven by power supplies (Wavelength Electronics, Inc.,Bozeman, USA), and monochrome CCD cameras (Pantera 1M30, DALSA, Gröbenzell, Germany) attached to a stereomicroscope (MZ12.5, Leica Microsystems,Wetzlar, Germany).
Nikon Fn1 fluorescence workstation
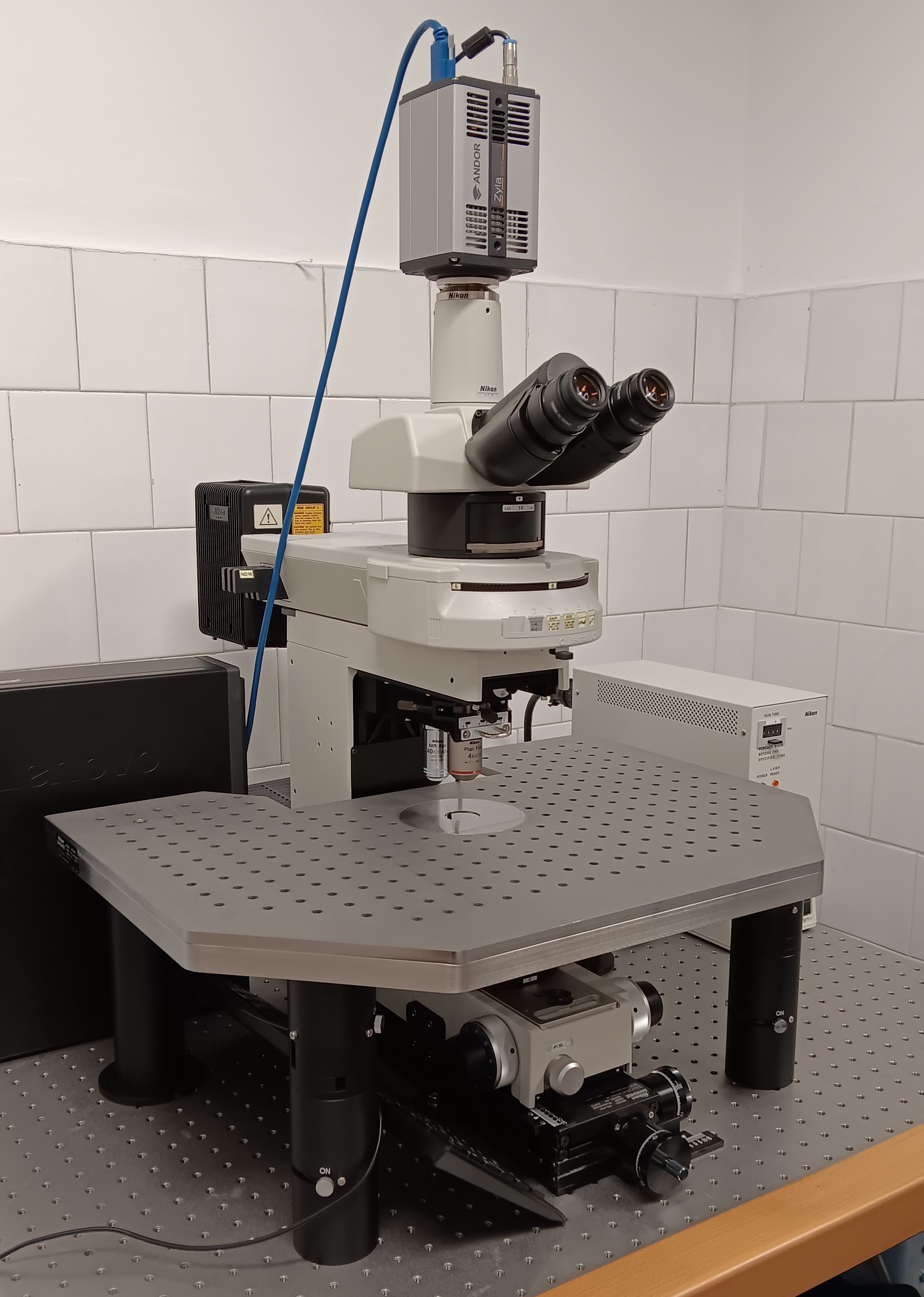 The workstation sits on a vibration-free table and can be upgraded to a patch clamp workstation.
The workstation sits on a vibration-free table and can be upgraded to a patch clamp workstation.
Technical description:
Nikon Fn1 microscope: Stable upright microscope frame, Eyepiece: 22 mm field of view, 10x magnification, Objective changer: 2-slot slider for 60 mm parfocal distance objectives, Laser confocal scanning head, Nikon C2+ A1+ matched IR polarizer, Condenser: long working distance, 0. 78 NA and 7.2 mm working distance, Polarizer/analyzer: optimized for 850-950 nm wavelength, Pre-centered lamp housing: 100W halogen light source, CFI Plan Fluor 4XA, N.A. 0.13, W.D. 17.1mm, Long working distance Apo 40×W IR, optimized for N.A.0 .8, working distance 3.5 mm, Fluor illumination: 100W mercury vapor light source, Fluorescent filter blocks: FITC, Texas RED for marking.
Andor Zyla microscope camera: Camera resolution: 2048 x 2048 pixels, Camera sensor type: 4.1 Megapixel resolution, monochrome sCMOS, Maximum readout speed: 53 fps. at full resolution, Pixel size: 6.5µm x 6.5µm for still and video images, Readout noise: 0.9 eDynamic range: 33.000:1
Neuroimaging Research Group, Department of Radiology, Albert Szent-Györgyi Medical School, University of Szeged, Hungary
HUN-REN BRC Institute of Biophysics, Neurovascular Unit Research Group, Hungary
STED, superresolution microscope
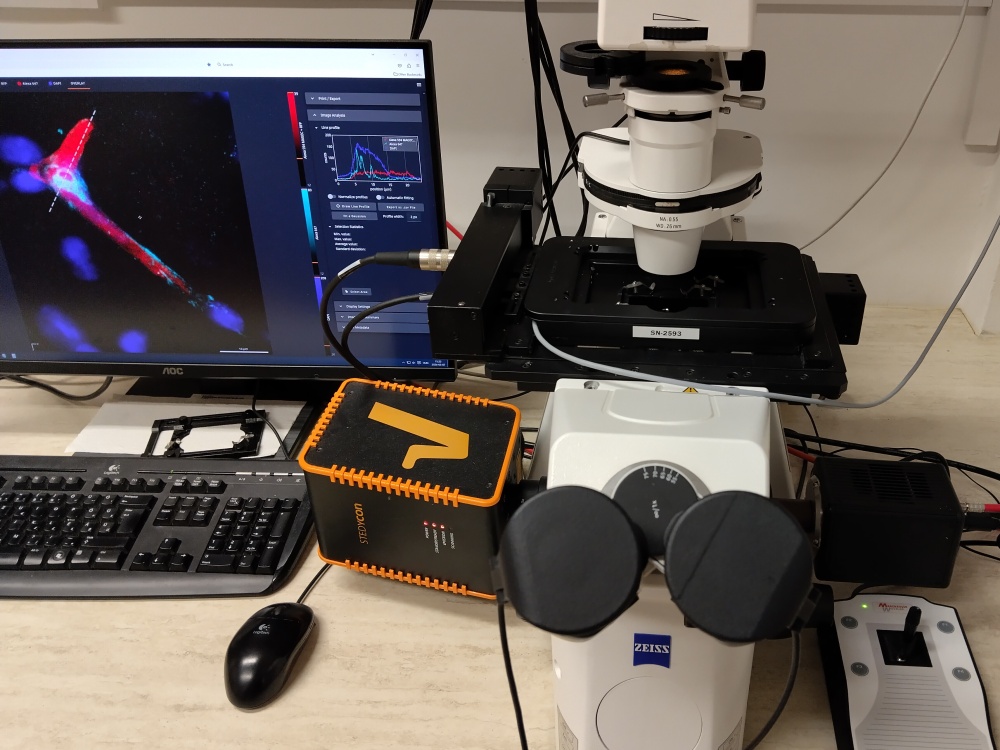 Our Stedycon (Abberior Instruments) superresolution capable STED module is attached to an Axio Observer.Z1 inverted epifluorescent microscope (Zeiss). The best optical resolution, that is <40 nm can be achieved using fluorophores that emit in the 650-700 nm interval. At the same time nearly as good resolution images can be taken at 578-628 nm and classical confocal resolution (approx. 250 nm) for green and blue fluorophores. Avalanche photodiodes quantify the emitted light and impulse lasers emitting at 640 nm, 561 nm, 488 nm and 405 nm are responsible for excitation. Stimulated emission depletion is achieved by a 775 nm impulse laser. STED imaging requires the use of the 1.46 NA 100x oil immersion objective, field of view is 90 µm x 80 µm. We recommend to use highly photostable fluorophores (such as the Star series of dyes available from Abberior); however other dyes such as the red and far red Alexa family dyes were already used successfully, although at slightly lesser resolution (50-60 nm).
Our Stedycon (Abberior Instruments) superresolution capable STED module is attached to an Axio Observer.Z1 inverted epifluorescent microscope (Zeiss). The best optical resolution, that is <40 nm can be achieved using fluorophores that emit in the 650-700 nm interval. At the same time nearly as good resolution images can be taken at 578-628 nm and classical confocal resolution (approx. 250 nm) for green and blue fluorophores. Avalanche photodiodes quantify the emitted light and impulse lasers emitting at 640 nm, 561 nm, 488 nm and 405 nm are responsible for excitation. Stimulated emission depletion is achieved by a 775 nm impulse laser. STED imaging requires the use of the 1.46 NA 100x oil immersion objective, field of view is 90 µm x 80 µm. We recommend to use highly photostable fluorophores (such as the Star series of dyes available from Abberior); however other dyes such as the red and far red Alexa family dyes were already used successfully, although at slightly lesser resolution (50-60 nm).
Two-photon, intravital microscope
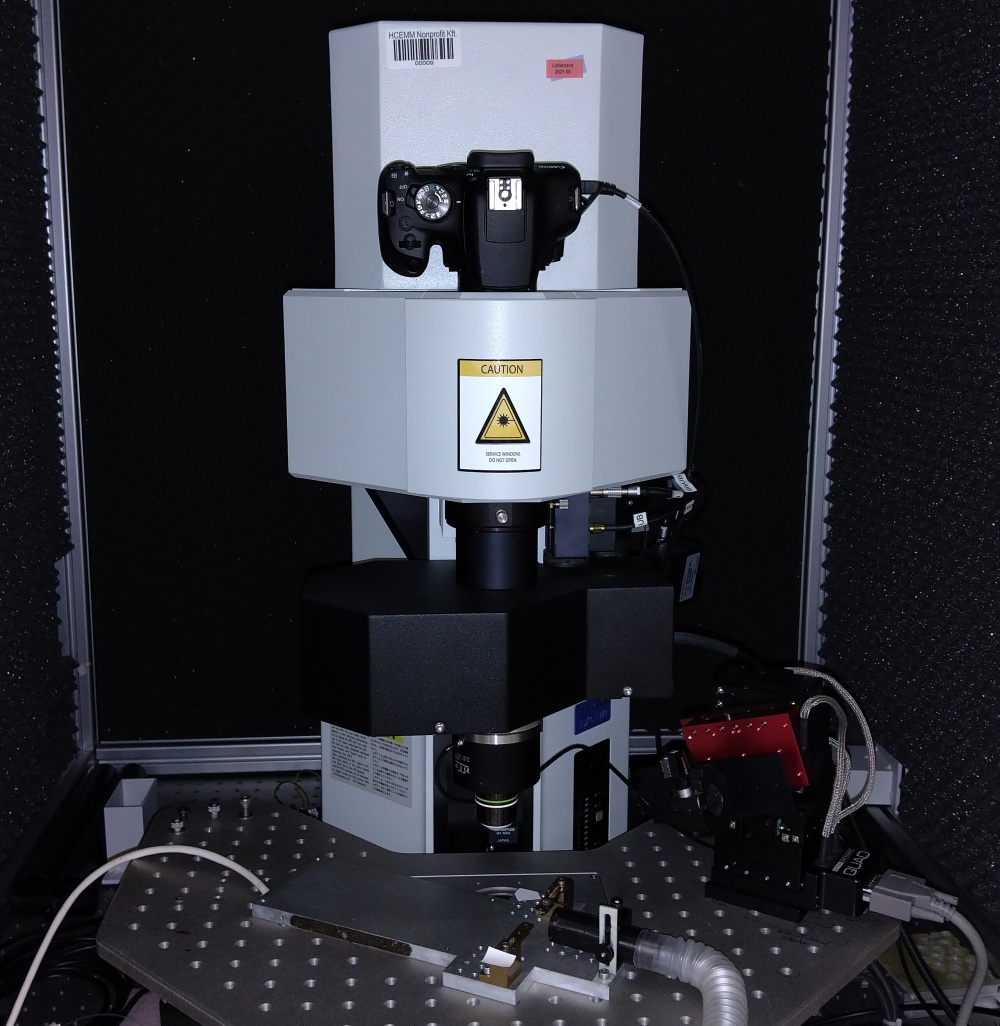 Our FEMTO 3D Dual (Femtonics) two-photon microscope can take intravital fluorescent images, Z-stacks, line scans or volume scans at approximately 400 nm resolution using long distance 20x and 60x water immersion objectives. With the 20x objective, 700 * 700 um images can be recorded at 1-2 Hz using a galvanometric scanner or at 30 Hz using a resonant scanner. Excitation is performed by a femtosecond Ti/sapphire laser (Spectra-Physics) tuneable in the 690-1040 nm range. Emitted fluorescence is detected by three photomultipliers behind optical filter cubes appropriate for blue, green and red fluorescence. Optogenetic activation is available through the use of a 473 nm diode laser. Mice can be placed under the objective under isoflurane anaesthesia. Body temperature is maintained with a heating pad with a headpost.
Our FEMTO 3D Dual (Femtonics) two-photon microscope can take intravital fluorescent images, Z-stacks, line scans or volume scans at approximately 400 nm resolution using long distance 20x and 60x water immersion objectives. With the 20x objective, 700 * 700 um images can be recorded at 1-2 Hz using a galvanometric scanner or at 30 Hz using a resonant scanner. Excitation is performed by a femtosecond Ti/sapphire laser (Spectra-Physics) tuneable in the 690-1040 nm range. Emitted fluorescence is detected by three photomultipliers behind optical filter cubes appropriate for blue, green and red fluorescence. Optogenetic activation is available through the use of a 473 nm diode laser. Mice can be placed under the objective under isoflurane anaesthesia. Body temperature is maintained with a heating pad with a headpost.


